Chromatic and Monochromatic Optical Aberrations
Designing optical systems is never an easy task; even perfectly designed systems contain optical aberrations. The trick is in understanding and correcting for these optical aberrations in order to create an optimal system. To do so, consider the types of aberrations present in optical systems.
Optical aberrations are deviations from a perfect, mathematical model. It is important to note that they are not caused by any physical, optical, or mechanical flaws. Rather, they can be caused by the lens shape itself, or placement of optical elements within a system, due to the wave nature of light. Optical systems are typically designed using first order or paraxial optics in order to calculate image size and location. Paraxial optics does not take into account aberrations; it treats light as a ray, and therefore omits the wave phenomena that cause aberrations.
Optical aberrations are named and characterized in several different ways. For simplicity, consider aberrations divided into two groups: chromatic aberrations (present when using more than one wavelength of light) and monochromatic aberrations (present with a single wavelength of light).
CHROMATIC ABERRATIONS
Chromatic aberrations are further classified into two types: transverse and longitudinal. Longitudinal can then be either primary or secondary longitudinal chromatic aberration.
Transverse chromatic aberration (TCA) occurs when the size of the image changes with wavelength. In other words, when white light is used, red, yellow, and blue wavelengths focus at separate points in a vertical plane (Figure 1). In optical terms, 656.3nm (red) is referred to as C light, 587.6nm (yellow) as d light, and 486.1nm (blue) as F light. These designations arise from their hydrogen emission lines for C & F lights and helium for d light.
Longitudinal chromatic aberration (LCA) occurs when different wavelengths focus at different points along the horizontal optical axis as a result of dispersion properties of the glass. The refractive index of a glass is wavelength dependent, so it has a slightly different effect on where each wavelength of light focuses, resulting in separate focal points for F, d, and C light along a horizontal plane (Figure 2).

Figure 1: Transverse Chromatic Aberration of a Single Positive Lens
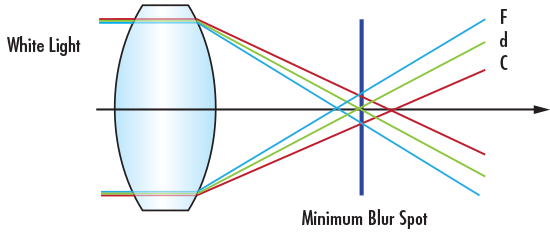
Figure 2: Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration of a Single Positive Lens
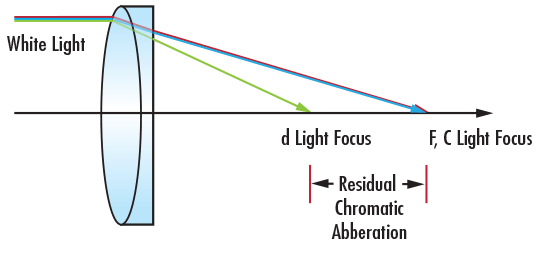
Figure 3: Achromatic Doublet Lens Correcting for Primary Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration
Primary LCA correction is usually performed using an achromatic doublet lens, which is made of positive and negative lens elements of different refractive indices (Figure 3). This type of correction forces F and C light to focus at the same place, but has little effect on the location of the d light focus, which leaves residual chromatic aberration.
In order to correct this residual LCA, a more complex lens or lens system must be used to shift the focus of d light to be at the same axial location as the F and C focus. This type of correction is usually achieved by using an apochromatic lens, which is corrected such that three wavelengths focus at the same point, or a superachromatic lens, which is corrected such that four wavelengths focus at the same point. Figures 4a – 4d show a comparison in focus shift between the aforementioned types of lens systems.
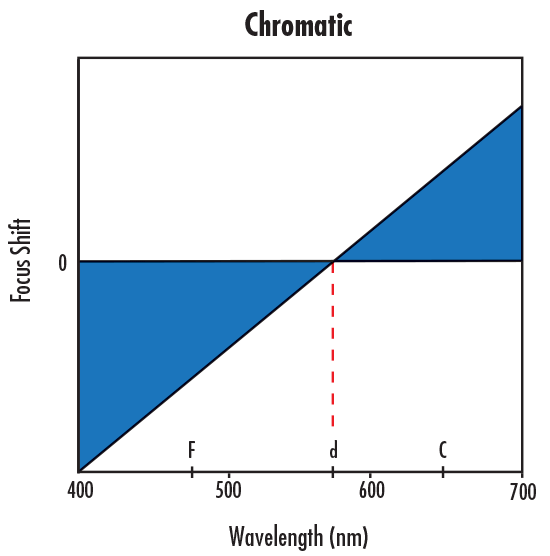
Figure 4a: Focus Shift Illustration of No Aberration Correction with a Singlet Lens

Figure 4b: Focus Shift Illustration of Primary Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration Correction with an Achromatic Lens
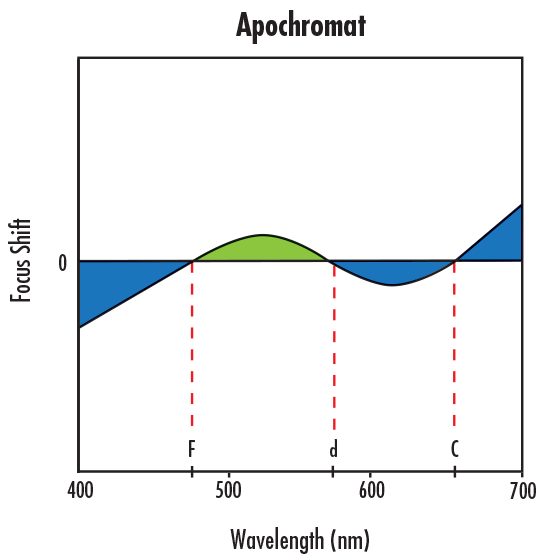
Figure 4c: Focus Shift Illustration of Secondary Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration Correction with an Apochromatic Lens
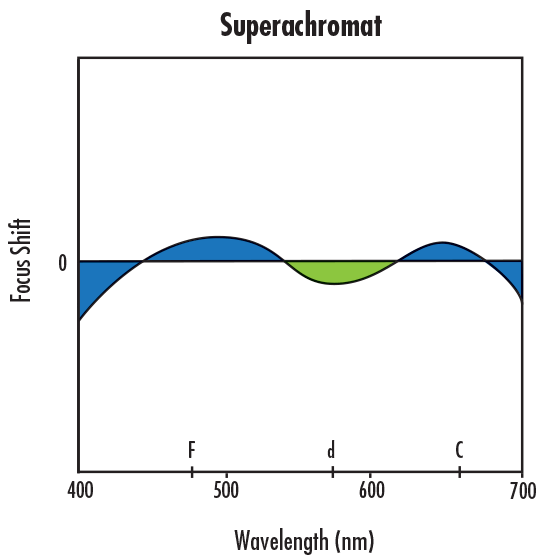
Figure 4d: Focus Shift Illustration of Secondary Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration Correction with a Superachromatic Lens
MONOCHROMATIC ABERRATIONS
By far, monochromatic aberrations outnumber chromatic aberrations. Therefore, they are labeled with wavefront coefficients in addition to names. For example, spherical aberration has a wavefront coefficient of W040. This wavefront coefficient arises from the mathematical summation that gives the actual difference between the perfect and aberrated wavefronts:
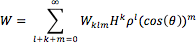
In Equation 1, Wklm is the wavefront coefficient, H is the normalized image height, ρ is the location in the pupil, and θ is the angle between the two, which arrives due to the dot product of the two vectors. Once the wavefront coefficient is known, the order number can be determined by adding l and k. However, this will always create an even number. Since optical aberrations are often referred to as first, third, fifth order, etc, if k + l = 2, it is a first order aberration, if k + l = 4, it is a third order, etc. Generally, only first and third order aberrations are necessary for system analysis. Higher order aberrations exist, but are not commonly corrected in optical systems because of the complication this adds to the system. Usually, the complexity of correcting higher order aberrations is not worth the image quality improvement. Common third order monochromatic aberrations and their corresponding coefficients and equations are listed in table 1.
Aberration Name | Wavefront Coefficient | Equation |
|---|---|---|
Tilt | W111 | W111Hρcos(θ) |
Defocus | W020 | W020ρ2 |
Spherical | W040 | W040ρ4 |
Coma | W131 | W131Hρ3cos(θ) |
Astigmatism | W222 | W222H2ρ2cos2(θ) |
Field Curvature | W220 | W220H2ρ2 |
Disortion | W311 | W311H3ρcos(θ) |
Table 1: Common Third Order Optical Aberrations
Optical and imaging systems can contain multiple combinations of optical aberrations. These optical aberrations can be classified into either chromatic or monochromatic. Aberrations will always degrade image quality, and a very large portion of optical design is focused on recognizing and reducing these aberrations. The first step in correcting for aberrations is to understand the different types and how they affect system performance. With this knowledge, one can then design the best system possible. For in-depth information on identifying and correcting for chromatic and monochromatic aberrations, view Comparison of Optical Aberrations.
版權(quán)所有 © 2025 江陰韻翔光電技術(shù)有限公司 備案號:蘇ICP備16003332號-1 技術(shù)支持:化工儀器網(wǎng) 管理登陸 GoogleSitemap